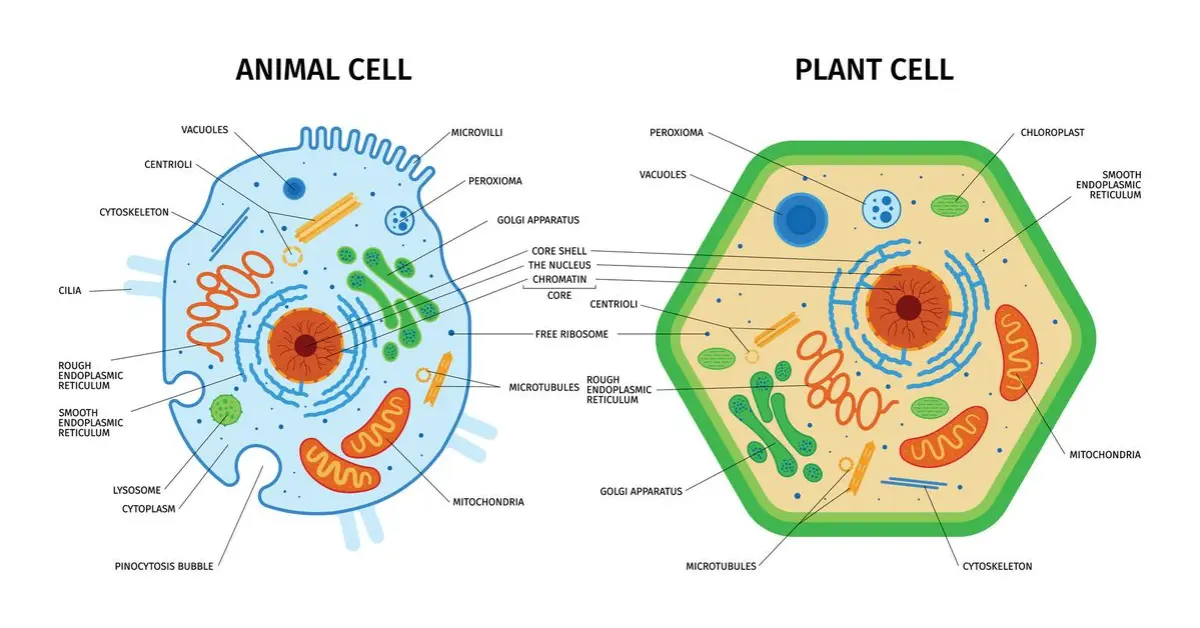
Cells are the building blocks of all living things. Whether it is a tall mango tree, a small green leaf, a human being, or a tiny ant—everything is made of cells. But not all cells are the same. Two of the most common types of cells studied in school biology are plant cells and animal cells. Understanding the difference between plant and animal cell is important because it helps us learn how different organisms live, grow, and function.
This article explains the topic in an easy and simple way, suitable for beginners and also helpful for students searching for difference between plant cell and animal cell class 8. We will cover what is the difference between plant cell and animal cell, list the 10 differences between plant and animal cells, and also provide additional explanations to build strong conceptual understanding.
What Is a Plant Cell?
A plant cell is the basic unit of life in plants. It is eukaryotic, which means it has a true nucleus and membrane-bound organelles. Plant cells are special because they have structures that help plants make their own food through photosynthesis.
Key features of a plant cell:
- Has a cell wall made of cellulose
- Contains chloroplasts for photosynthesis
- Has a large central vacuole
- Usually rectangular or box-like in shape
What Is an Animal Cell?
An animal cell is the basic structural and functional unit in animals. Like plant cells, animal cells are also eukaryotic, but they lack some structures found in plant cells.
Key features of an animal cell:
- Does not have a cell wall
- Does not have chloroplasts
- Contains small vacuoles
- Usually round or irregular in shape
Also Read: Difference Between Salon and Saloon
10 Differences Between Plant and Animal Cells
Here are 10 differences between plant and animal cells explained simply and clearly:
1. Cell Wall
- Plant cell: Present (made of cellulose)
- Animal cell: Absent
The cell wall gives plants strength and shape.
2. Chloroplasts
- Plant cell: Present for photosynthesis
- Animal cell: Absent
This is why animals cannot make their own food.
3. Shape
- Plant cell: Fixed, rectangular
- Animal cell: Round or irregular
The cell wall helps maintain shape in plants.
4. Vacuoles
- Plant cell: One large central vacuole
- Animal cell: Many small vacuoles
The large vacuole stores water and nutrients in plant cells.
5. Mode of Nutrition
- Plant cell: Autotrophic (makes food)
- Animal cell: Heterotrophic (depends on others for food)
Chloroplasts help plants make food through photosynthesis.
Read More: Difference Between Brontosaurus and Brachiosaurus
6. Centrosomes
- Plant cell: Usually absent
- Animal cell: Present and helps in cell division
7. Lysosomes
- Plant cell: Rare
- Animal cell: Common
Lysosomes help in digesting waste materials.
8. Energy Storage
- Plant cell: Stores energy as starch
- Animal cell: Stores energy as glycogen
9. Nucleus Position
- Plant cell: Pushed to the side because of large vacuole
- Animal cell: Located in the center
10. Size
- Plant cells: Usually larger
- Animal cells: Usually smaller
Detailed Explanation of the Differences
While listing differences is helpful, understanding why they exist makes learning meaningful. Below is a deeper explanation in simple words.
1. Why Do Plants Have a Cell Wall?
Plants cannot move from one place to another. The cell wall helps them:
- Stand upright
- Resist wind and pressure
- Protect inner structures
Animals do not need such support because they have muscles, bones, and flexible tissues.
2. Importance of Chloroplasts
Chloroplasts contain chlorophyll, a green pigment that absorbs sunlight to make food. This process is called photosynthesis. Because animals cannot perform photosynthesis, they do not have chloroplasts.
3. Vacuole Size Difference
Plant cells need a large vacuole to:
- Store water
- Maintain pressure
- Keep leaves firm (turgidity)
Animal cells have smaller vacuoles because they do not need such strong water regulation.
4. Nutrition Mode
Plants are autotrophs, meaning they prepare their own food.
Animals are heterotrophs and depend on plants or other animals for food.
This nutritional difference also affects cell structure.
5. Cell Division Differences
Animal cells contain centrioles that help in cell division.
Plant cells mostly divide using the cell plate method.
Table: Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell
| Feature | Plant Cell | Animal Cell |
|---|---|---|
| Cell Wall | Present | Absent |
| Chloroplast | Present | Absent |
| Vacuole | One large vacuole | Many small vacuoles |
| Shape | Rectangular | Irregular or round |
| Nutrition | Autotrophic | Heterotrophic |
| Lysosomes | Rare | Present |
| Centrioles | Generally absent | Present |
| Energy Storage | Starch | Glycogen |
| Nucleus Position | Side | Center |
| Size | Larger | Smaller |
Why Understanding the Differences Matters
1. How different organisms survive
Plants can make their own food, but animals cannot.
2. How ecosystems work
Plants act as producers and animals act as consumers.
3. Medical and agricultural science
Understanding cell structure helps scientists create better medicines, food crops, and treatments.
4. Foundation for higher biology
Cell biology forms the base of topics like genetics, botany, zoology, and biotechnology.
Scientific References (Trusted Sources)
These references support the information presented:
- Campbell Biology – Neil A. Campbell & Jane Reece (Pearson Education)
- NCERT Class 8 Science Textbook – Chapter: Cell Structure and Functions
- Biology by Sylvia S. Mader (McGraw-Hill Education)
- OpenStax Biology, Rice University – Free educational resource
Conclusion
Plant cells and animal cells are similar in many ways, but they also have important differences that help them perform their unique roles. Plant cells have a cell wall, chloroplasts, and a large central vacuole, while animal cells have centrosomes, lysosomes, and flexible shapes. Understanding these differences helps us appreciate how life varies across the plant and animal kingdoms.
Whether you are studying for school exams, especially difference between plant cell and animal cell class 8, or simply curious about biology, knowing what is the difference between plant cell and animal cell builds a strong foundation for future learning.